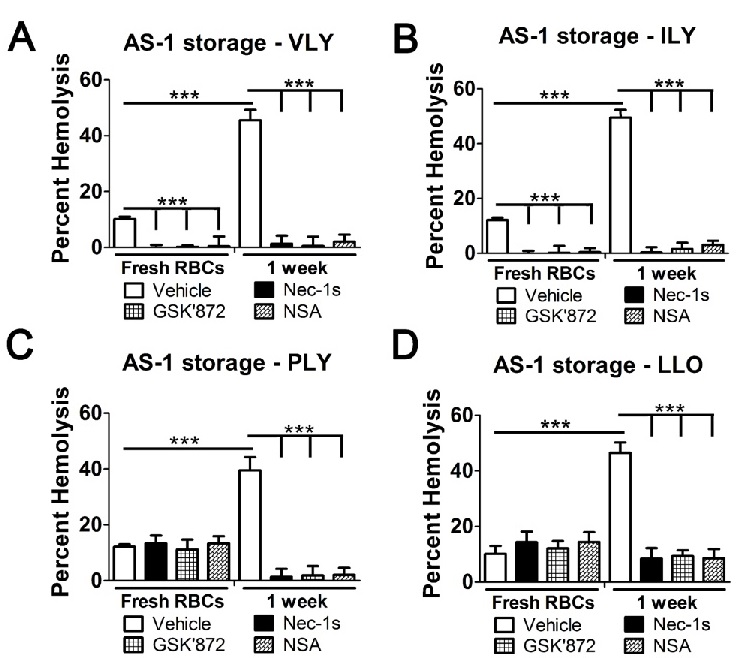
Fig. 2. Storage in AS-1 leads to increased RBC necroptosis. Fresh human RBCs or those stored in AS-1 for 1 week were treated with the necroptosis-inducing A.) VLY, B.) ILY and the non-necroptotic C.) PLY and D.) LLO. The necroptosis-inducing toxins VLY and ILY (A-B) produce RBC death that can be inhibited by nec-1s (RIP1 inhibitor), GSK'872 (RIP3 inhibitor), or necrosulfonamide (NSA, MLKL inhibitor). This RBC necroptosis increases following 1 week of storage in AS-1 relative to fresh RBCs. The non-necroptotic toxins PLY and LLO (C-D) produced death of fresh RBCs that was not inhibited by nec-1s, GSK'872, or NSA. However, following 1 week of storage in AS-1 RBC death by PLY and LLO was prevented by nec-1s, GSK'872, and NSA. Hemolysis values were normalized to basal RBC death in the absence of toxin treatment. Results shown are from 3 independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA, ***p<0.001.